9.1 What is ZooKeeper
ZooKeeper is all about implementing distributed system using Hadoop. If one sender and receiver are communicating and due to some reason network fails then following things would happen –
- Sender has no idea of receipt receive the message
- Receiver may not have received at all
- Receiver’s process might have died
ZooKeeper never ever makes partial failures (Where we are not aware of whether failure took place or not). ZooKeeper provides you set of utility so that you can handle partial failures safely.
Following are the characteristics of ZooKeeper –
- ZooKeeper remains highly available in the way it helps you to avoid single point of failure
- ZooKeeper support an interaction where participants aren’t required to be known to each other
Zookeeper is Hadoop’s coordination service which is distributed in nature. Zookeeper provides a platform where processes that do not know about each other’s presence and existence come together and get to know each other. Even they come to know about their network detail.
Performance wise Zookeeper is really very good. Zookeeper was created at Yahoo, they have tested its performance and found benchmark performance of per second 10,000 operations. Note that this was for the WRITE kind of workload and opposite to this where workload is of READ in nature, the throughput s very high.
9.2 ZooKeeper Installation And Configuration
Make sure that JAVA 6 is there in your machine since ZooKeeper requires it to run.
Download a ZooKeeper release from Apache website. Unzip the file at your suitable directory. ZooKeeper provides some binaries.
Before actually running the ZooKeeper service. As a convention this file is called as the zoo.cfg. We need to set some JAVA properties in the file, these are –
- tickTime
- dataDir
- clientPort
To check ZooKeeper is running, use Imok command and to which ZooKeeper will respond as (If ZooKeeper is running fine)
- Imok (meaning “I am OK”)
Following are the other “four letter word” commands for managing ZooKeeper ->
Command | Description |
Ruok | If the server is running and not in error state then will print imok |
Conf | It prints the server configuration from zoo.cfg |
Envi | It prints the server environment detail –
|
Srvr | Prints the server statistics –
|
Stat | It prints –
|
Srst | To reset server statistics |
Isro | This command shows whether the server is in read-only mode or readwrite mode |
dump | To lists all the sessions |
cons | It lists connection statistics for all the server’s clients |
Crst | Resets connection statistics |
wchs | It lists summary information for the server’s watches |
wchc | Lists all the server’s watches by connection |
wchp | Lists all the server’s watches by znode path |
mntr | It lists server statistics in Java Properties format |
9.3 Understand the Basics of ZooKeeper
In a distributed environment, ZooKeeper maintains the list of servers and locates the required server to client easily. This helps lot as you will find lot of servers in a distributed environment.
In a distributed environment, ZooKeeper maintains the list of servers and locates the required server to client easily. This helps lot as you will find lot of servers in a distributed environment.
Suppose there is a network application running where a client dealing with multiple servers and each server is responsible for some of the services. The requirement is that client should be able to access a particular so that to access particular service. The biggest challenge in is that we do not have servers listing in the group. If we keep all list in a single server node then it would become a single point of failure and we definitely don’t want to do that. Our requirement is that we always want this list to be highly available. Suppose a server fails then we want a standard mechanism for removing a failed server from the network as the failed server cannot remove itself. Note that here we are talking about an active data structure which is distributed in nature. We want a standard mechanism to automate the things and take decision based on the occurrence of some event.
The biggest thing that Zookeeper offers is as it provides all these sorts of services and it makes Zookeeper unique in nature, highly performant and efficient in working.
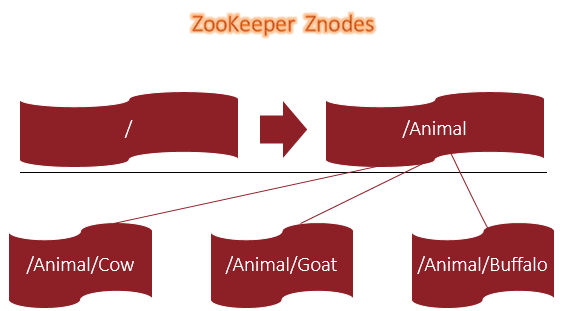
Another way of understand Zookeeper is to imagine it as a file system which is high available in nature. It does not have files as well as directories but support a unique node based concept known as znode. It acts as a file which is a container to keep the data along with this is also acts as directory where it maintains or contains other znode information. Actually znode prepares a namespace which is hierarchical in nature.
In znode, membership list gets created in a very unique and natural way. Very first it creates a parent znode that has the group name followed by child znode which includes the group member’s name.
9.4 Administration through ZooKeeper
In the entire Hadoop’s Eco System the administrative part takes care by ZooKeeper. It remains the part of entire client server network and perform administration. ZooKeeper has a concept of ZNODE.
Let us have look at below example where we won’t be storing data in any of the znodes. Example =>