7.1 INTRODUCTION TO SERVLETS ENVIRONMENT SETUP
We have discussed about the concepts of Servlets in earlier chapters and now we will start implementing what we have learned.
To develop and run any web applications, we need to have development environment up and running which means we have to have all required software installed on machine. In this chapter we will discuss how to set up development machine.
We will follow below steps to complete the set up.
- Download and install Java.
This step involves downloading and installing Java 7 , setting up environment variables (JAVA_HOME and PATH) appropriately. It is covered in Section 7.2.
- Download and configure Apache Tomcat web server.
This step involves downloading a server that implements the JSP and Servlet
APIs. It is covered in Section 7.3
- Integrated Development Environment Set Up
This step involves installation of Eclipse IDE. Refer section 7.4 for more details.
- Tomcat Integration with Eclipse
This section is more of integration of tomcat with Eclipse so it can be managed from eclipse itself. Details available in section 7.5
- Test your setup.
This step involves verification of the installation.
7.2 DOWNLOAD AND INSTAL JAVA
Java comes with two editions (Standard Edition J2SE and Enterprise Edition J2EE ).For JSP and servlets we requires Standard Edition (J2SE) but for other J2EE features like EJB, JMS etc , we would need Enterprise Edition(J2EE).
This entire tutorial is based on JSP and Servlets so we would need J2SE edition.
Java is available for download for all operating systems on Oracle’s Java website and you can download it from http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads
Below steps will install both JDK and JRE.
As Windows Operating system is very popular so all the instructions are for Windows platform.
(refer below figure).

Downloaded file is an exe file so you just need to install it. This is quite simple but one thing that you need to do is setting the environment variables.
Below are the screens that you will see while installing Java on your machine.
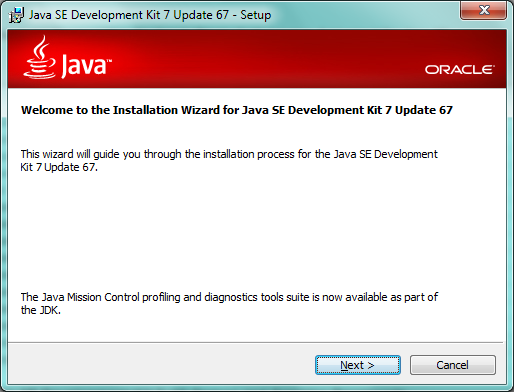
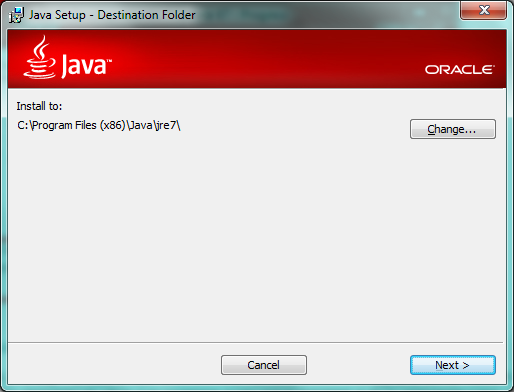
Change the path on next screen if you want to (highlighted in below figure)

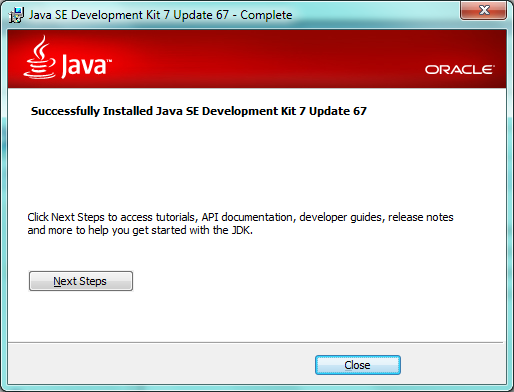
Click Close.
Now you need to create and update below environment variables.
a)JAVA_HOME – Create a new environment variable JAVA_HOME and set its value to the installation directory of Java. For example if you have installed it in “C:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jdk1.7.0_67“ , you need to set its value as C:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jdk1.7.0_67
b) PATH- This is an existing environment variable and you just need to update it. Add the JAVA_HOME variable with bin.
Example – if JAVA_HOME is set to C:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jdk1.7.0_67 then Path variable will be updated with
PATH=%PATH%;C:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jdk1.7.0_67/bin;
Alternatively
PATH=%PATH%;%JAVA_HOME%/bin;
You don’t know where to set the environment variable? No Problem. On windows platform –
Right Click On My ComputeràPropertiesàAdvanced system settingsàEnvironment Variables
You can add it either as a User variable or a system variable. Only difference is that System Variables will be available to all users of the system.
Other way is to add below lines in C:\autoexec.bat
set JAVA_HOME= C:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jdk1.7.0_45
set PATH=%PATH%;%JAVA_HOME%/bin;
Note - C:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jdk1.7.0_45 is example value. You need to use you own java installation directory path
Verification- Once java is installed and environment variables are updated, open a command prompt and type a java . If everything is correct, it will show you several java options (refer below figure)

7.3 DOWNLOAD AND CONFIGURE APACHE TOMCAT WEB SERVER.
There are several web and application servers available and all of them supports JSP and servlets (means they all have JSP and servlet containers). As we are not using any advanced J2EE components like EJB, JMS we would need web server and not application server.
For web servers also there are several options but among all Apache Tomcat is very popular.
Tomcat is actually composed of a number of components and containers including a Tomcat JSP engine, servlet Container and a variety of different connectors, but its core component is called Catalina. One important thing to be noted is Tomcat is a web server and not an application server.
Tomcat is freely available and can be downloaded from http://tomcat.apache.org/download-70.cgi
Note – There are several versions of tomcat and java are available so make sure you download compatible versions.
Steps to download and configure Tomcat
- Once tomcat web server is downloaded, unzip it to the location of your choice. I use the top level of the D drive, resulting in D:\apache-tomcat-7.0.41 . By default tomcat is configured to run on port 8080 so it will be accessed by http://localhost:8080
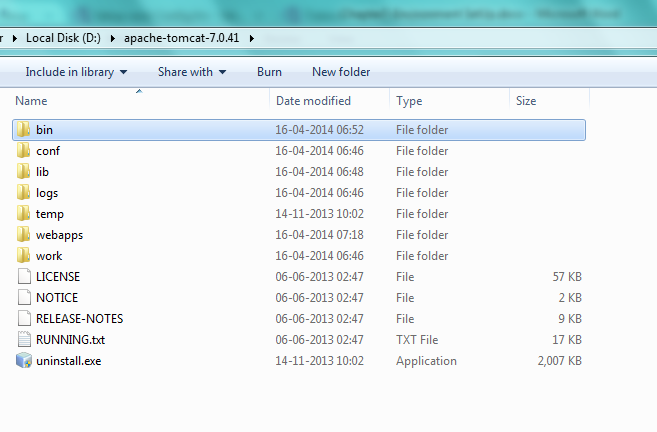
- Create a new environment variable CATALINA_HOME and set its value to the apache tomcat installation directory. In my case it will be D:\apache-tomcat-7.0.41
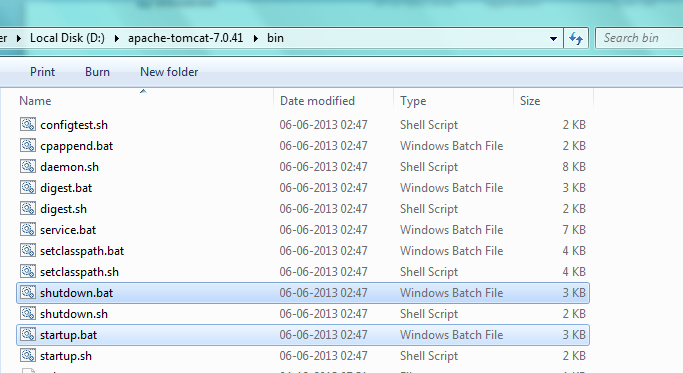
- To start and stop the server, you need to use the batch files available in %CATALINA_HOME%/bin
- startup.bat to start the server
- shutdown.bat to stop the server
If you hit an error while starting server a saying “java_home /jre_home” is not set means you have not configured JAVA_HOME as described in section 7.2
Verification
Start the server using D:\apache-tomcat-7.0.41/bin/startup.bat and hit http://localhost:8080 in the browser. You should see page like below.

7.4 INTEGRATED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT SETUP
We can develop java program or web application using any text editor but several IDE are freely available. With the IDE,
- we can manage the Tomcat,
- develop programs and web application
- need not to remember the exact methods and their signatures
- compilation errors are clearly highlighted
which means it improves our efficiency.
There are several IDEs available like NetBeans, Eclipse etc. We will use Eclipse in the servlet tutorial.
Download Eclipse Kepler which is most latest and stable version of eclipse IDE http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/packages/release/Kepler/SR2 and unzip it in directory of your choice . You need to download Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers and not Eclipse Standard
I normally unzip into the top level of the D drive, resulting in D:\ eclipse-standard-kepler-SR2-win64
Start Eclipse – Start eclipse by clicking eclipse.exe available in eclipse installation directory.
Once eclipse starts it will ask for a workspace. You can create one folder of your own choice and give the path of that folder. Workspace is basically a folder where eclipse will create all of your projects.
7.5 TOMAT INTEGRATION WITH ECLIPSE
As I mentioned earlier, tomcat can be managed with eclipse IDE and in this section we will discuss how to integrate tomcat with eclipse.
To do so
- Go to Windows àPreferencesàServersàRuntime Environments àAdd in eclipse.
- On click of Add , a new window will be opened (refer below). From the list of Tomcat servers, select “Apache Tomcat v7.0” and click Next

- Select the path of Tomcat installation directory

Start and Stop Tomcat server from Eclipse
Click on Servers tab at bottom. Click on Green Arrow icon to start the server and Red square icon to stop.
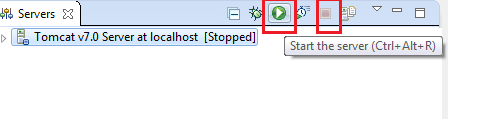
Server console log can be seen in eclipse console. Once server is started, verify it by hitting http://localhost:8080 in browser.
